Get a quoate
What is ISO 14644 Standards? A Comprehensive Guide to Cleanroom Classes
Published : 2026-01-11Core Concepts of the ISO 14644 Standard
ISO 14644 is a set of international standards established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) for cleanrooms and related controlled environments. Its core function is to provide unified, quantifiable guidelines for the design, construction, operation, and maintenance of cleanrooms globally, eliminating discrepancies in standards across different countries and regions while reducing technical barriers to international trade. Simply put, it serves as the “universal international benchmark” for the cleanroom industry, covering the entire lifecycle from design planning to long-term operation and maintenance.
In terms of core content, the standard can be broken down into three key modules: First, the classification of cleanliness grades. This forms the core of the standard, categorizing cleanrooms into nine grades from ISO Class 1 (highest cleanliness) to ISO Class 9 (lowest cleanliness) based on the maximum allowable number of suspended particles of specific sizes (≥0.1μm) per cubic meter of air. The particle limits for each core grade are shown in the table below:
| ISO Cleanliness Class | Particle count ≥0.1μm (particles/m³) | Particle count ≥0.2μm (particles/m³) | Particle count ≥0.5μm (particles/m³) | Particle count ≥5.0 μm (particles/m³) | Common Application Scenarios |
| ISO Class 3 | 100 | 24 | 10 | 0 | Semiconductor lithography, high-end electronic component manufacturing |
| ISO Class 5 | 10000 | 2370 | 352 | 0 | Sterile filling for biopharmaceuticals, precision instrument assembly |
| ISO Class 7 | 1000000 | 237000 | 35200 | 293 | General electronics assembly, medical device manufacturing |
| ISO Class 8 | 10000000 | 2370000 | 352000 | 2930 | Ready-to-eat food packaging, cosmetics manufacturing |
Second, state differentiation: It clearly defines two testing states—“static” (equipment operation without personnel activity) and “dynamic” (normal production including personnel operation)—requiring cleanrooms to meet corresponding grade requirements in both states, as personnel activity is one of the primary sources of contamination in cleanrooms. Third, comprehensive process standardization: It covers details such as cleanroom testing methods, material requirements, HVAC system design, and monitoring frequency, forming a complete compliance system. boben Modular Cleanroom Manufacturers consistently adopts this standard as the core reference in designing modular cleanrooms, ensuring the international applicability of its products.
How should different industries select the appropriate ISO 14644 cleanliness class?
Answer: The core principle in selecting cleanroom grades is to align with industry process requirements—higher grades are not necessarily better. Both compliance and cost-effectiveness must be considered. Typical grade matching for different industries and their key control priorities are shown in the table below:
| Industry Sectors | Recommended ISO Cleanliness Class | Core Control Particle Size | Additional Requirements |
| Semiconductor (Lithography/Epitaxy) | ISO 1-3 | ≥0.1μm | High-precision temperature and humidity control (±0.5°C/±3%RH) |
| Biopharmaceuticals (Aseptic Filling) | ISO 5 (Dynamic) | ≥0.5μm | Microbial Control (≤5 CFU/m³) |
| Food Processing (Ready-to-Eat Packaging) | ISO Class 8 | ≥5.0μm | Prevent cross-contamination and enforce personnel hygiene protocols |
| General Electronics Assembly | ISO 7-8级 | ≥0.5μm | Anti-static design |
boben Modular Cleanroom Manufacturers provides customers with precise grade matching solutions tailored to the process parameters of different industries.Add us on WhatsApp: +8613862527051 Get a free quote and design proposal.
What is the relationship between ISO 14644 standards and GMP standards? Do they need to be met simultaneously?
Answer: These standards operate on different dimensions and are not mutually exclusive. Most industries require compliance with both. ISO 14644 is a universal cleanroom technical standard, primarily quantifying environmental parameters like air cleanliness and airflow organization. GMP, however, is a production quality management specification for industries like pharmaceuticals and food, emphasizing end-to-end quality control throughout the production process. Its cleanroom requirements reference ISO 14644’s classification system (e.g., GMP’s Class A/B corresponds to ISO Classes 5-7). For instance, pharmaceutical companies must not only pass ISO 14644 cleanliness level testing but also comply with GMP requirements for personnel operations, material management, and validation procedures. Only through the integration of both standards can product quality and safety be ensured.
Core benefits of ISO 14644 standards?
For enterprises, strictly adhering to ISO 14644 standards is not an additional burden but a key measure to enhance core competitiveness. First, it ensures product quality stability. By precisely controlling airborne particle concentrations, it significantly reduces product scrap rates caused by contamination. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, compliance can boost chip yield rates by 10%-30%. Second, it lowers overall costs. The standard’s specifications for material selection and system design prevent resource waste from blindly pursuing higher grades or flawed designs, while also reducing future remediation and maintenance expenses. Third, it dismantles international trade barriers. As a globally recognized authoritative certification, compliant cleanrooms directly meet market access requirements across nations, facilitating corporate expansion into international markets. Finally, it enhances operational efficiency. The standard’s defined monitoring frequencies and maintenance procedures provide clear guidelines for cleanroom operations, minimizing production interruptions caused by environmental fluctuations.
Detailed steps for implementing ISO 14644 standards
To ensure a cleanroom complies with ISO 14644 standards, a full-cycle closed-loop process must be followed: Planning → Design → Construction → Testing → Operation & Maintenance. The specific steps are as follows:
- Preliminary Planning: Define core requirements, determine cleanliness levels and test conditions (static/dynamic) based on industry processes, and outline additional parameters like temperature, humidity, pressure differentials, and microbial limits. Develop a detailed technical specification. We recommend collaborating with specialized manufacturers. boben Modular Cleanroom Manufacturers offers preliminary assessment services to ensure requirements align with standards.
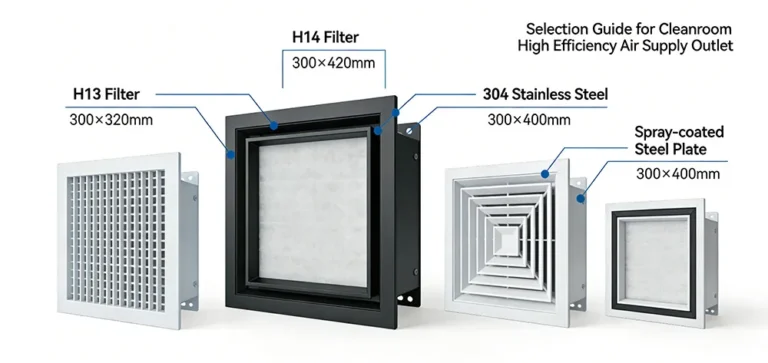
- Design Phase: Conduct targeted design based on cleanroom grade requirements, including: – Airtightness design for building envelope – HVAC airflow organization (e.g., vertical unidirectional flow for ISO Class 5) – Air change rate calculation (ISO Class 5 requires 200-400 changes/hour) – Personnel and material flow pathway planning – Selection of compliant materials (e.g., antimicrobial color-coated steel panels, H13 HEPA filters) A pre-assessment must be conducted after design completion to confirm the feasibility of the plan.
- Construction and Installation: Strictly execute according to the design plan, focusing on material installation precision (e.g., seamless color steel plate joints), system airtightness (preventing airflow short-circuiting), and equipment installation standards (e.g., uniform FFU layout). Conduct phased inspections during construction to promptly rectify issues such as insufficient airtightness or uneven airflow.
- Testing and Acceptance: Upon completion of construction, commission a third-party institution to conduct formal testing according to ISO 14644 standards. This includes particle concentration detection (sampling points arranged in a 0.5m × 0.5m grid, with three consecutive samples taken at each point and averaged), temperature and humidity testing, differential pressure testing, etc. All test data must meet the corresponding grade limits to pass acceptance and obtain the certification report.
- Operational Maintenance: Establish a routine management system to monitor temperature, humidity, and pressure differentials daily; inspect HEPA filter resistance changes weekly; clean air conditioning system filters monthly; replace pre-filters and HEPA filters every six months. Additionally, regularly calibrate monitoring instruments to ensure the cleanroom consistently meets standard requirements over the long term.
ISO 14644 Standard Practice Results Case Study
Case 1: ISO Class 5 Cleanroom Renovation for Biopharmaceutical Company
To meet international market access requirements, a vaccine manufacturer needed to upgrade its filling workshop to ISO Class 5 (dynamic). By adopting boben Modular Cleanroom Manufacturers’ modular solution, the project achieved standardized airflow optimization, VHP sterilization system integration, and intelligent monitoring platform implementation. Post-renovation third-party testing confirmed stable particle concentrations ≤1,200 particles/m³ for ≥0.5μm particles and microbial counts ≤5 CFU/m³, representing a 92% reduction from pre-renovation levels. The facility successfully passed ISO 14644 certification and GMP audits, achieving an annual output value increase of 230 million yuan.
Case 2: ISO Class 8 Cleanroom Operation and Maintenance Optimization for Food Packaging Enterprises
A ready-to-eat food company’s existing cleanroom experienced significant particle concentration fluctuations due to non-standardized operations. After implementing an ISO 14644-compliant maintenance system featuring regular equipment upkeep, personnel training, and environmental monitoring, Post-optimization, the workshop maintained stable particle concentrations below 20,000 particles/m³ for ≥5.0μm particles, meeting ISO Class 8 requirements. Food total bacterial count exceedance rates dropped from 3% to 0.2%, significantly boosting product compliance rates and enabling successful entry into the EU market.
For more case studies and solutions, add us on WhatsApp: +8613862527051 for free access.
Boben’s modular cleanroom solutions are developed precisely based on these standards. With 90% of testing completed in-factory, its prefabricated modules require only on-site assembly—reducing traditional six-month construction cycles to just three weeks. This innovation not only complies with ISO 14644-4 construction specifications but also lowers clients’ post-installation maintenance costs by 30% through modular design.