Get a quoate
How to Rapidly Expand Lab Capacity with Modular Mobile Cleanroom Solutions
Published : 2026-01-03Modular Mobile Cleanroom Solutions
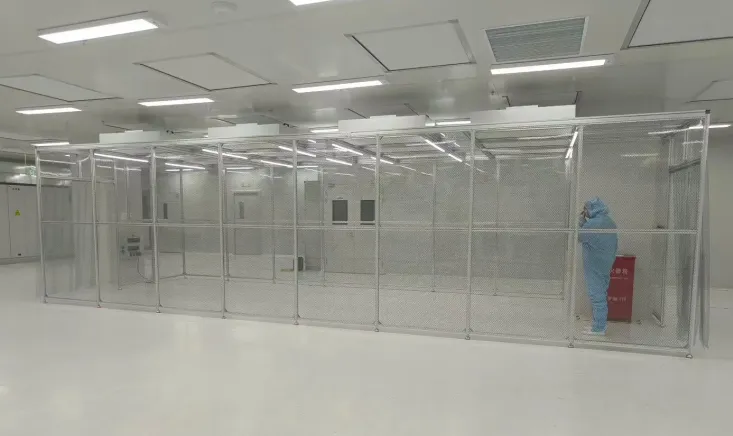
The Modular Mobile Cleanroom Solution is an advanced construction approach based on modular design principles. At its core are standardized, prefabricated cleanroom units, combined with flexible HVAC, purification, temperature, and humidity control systems. This solution enables the rapid assembly, relocation, and expansion of clean spaces. Its primary positioning is to resolve the pain points of traditional cleanroom construction—long cycles, difficult renovations, and poor flexibility—providing laboratories with “ready-to-use, adjustable-on-demand” clean space assurance for capacity expansion.

Decomposing its structure reveals three core modules:
- Prefabricated Cleanroom Unit Module: Featuring standardized dimensions (e.g., 3m×3m, 3m×6m), these units have their main structure, interior wall panels, and cleanroom doors/windows prefabricated in the factory, requiring no secondary on-site construction.
- Purification Assurance Module: Includes High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters, supply/return air systems, and differential pressure control systems to guarantee cleanliness levels (ranging from ISO Class 5/Class 100 to ISO Class 8/Class 100,000).
- Auxiliary Support Module: Covers electrical systems, lighting, disinfection systems, and monitoring systems to ensure normal laboratory operations.
Functionally, its core advantages lie in “Modular Combination” (unit quantity can be increased or decreased based on capacity needs) and “Mobile Flexibility” (equipped with bottom casters or lifting structures for easy relocation), all while meeting rigorous cleanroom performance standards.
Compared to traditional fixed cleanrooms, this solution is not merely a “movable clean space” but a complete capacity expansion package. It includes full-process services: pre-assessment, custom design, factory prefabrication, on-site deployment, and post-operation maintenance. It is particularly adapted for laboratories facing short-term capacity surges (e.g., emergency testing, project sprints) or long-term phased expansion needs.
Common FAQs Regarding Modular Mobile Cleanrooms
Q1: Can the cleanliness level of a modular mobile cleanroom meet the requirements of precision laboratory experiments?
A: Yes, absolutely. The core purification systems of modular mobile cleanrooms use technical configurations equivalent to traditional fixed cleanrooms. Cleanliness levels can be precisely customized based on lab needs, ranging from Class 100 (suitable for semiconductors and Biosafety Level 3 labs), Class 1,000, Class 10,000, to Class 100,000 (suitable for general chemistry and microbiological testing).
The purification principle is identical to traditional cleanrooms: utilizing a three-stage filtration system (Primary, Medium, and HEPA), combined with directional supply/return air structures to maintain positive pressure (preventing external contamination). Systems for differential pressure monitoring and temperature/humidity control ensure stable environmental parameters. For example, the mobile cleanroom units launched by Boben Modular Cleanroom Manufacturers utilize high-efficiency HEPA filters (efficiency ≥99.99% @ 0.3μm) and intelligent climate control to stably achieve Class 10,000 cleanliness, perfectly meeting the environmental requirements for molecular biology and drug R&D. In practice, this solution has been widely applied in medical testing and biopharmaceuticals, passing authoritative cleanliness certifications.
Q2: Does using modular mobile cleanrooms for rapid expansion increase post-maintenance difficulty and costs?
A: No, it actually reduces maintenance difficulty and costs.
- Standardization: Modular designs use highly interchangeable parts. Replacing consumables (like filters) or repairing equipment does not require custom, expensive parts, making procurement easier and cheaper.
- Intelligent Monitoring: Integrated systems monitor cleanliness, temperature, humidity, and pressure in real-time, alerting staff to anomalies immediately for quick resolution.
- Asset Flexibility: When capacity demand drops, idle units can be relocated to other scenarios or disassembled for storage, avoiding the resource waste of traditional “fixed-once-built” cleanrooms.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy consumption can be controlled independently for each unit based on usage, avoiding the waste of running a large traditional cleanroom for a small task. Long-term operations significantly lower costs.
- Support: Professional manufacturers (like Boben) provide operation training and after-sales support, further alleviating the maintenance burden on the laboratory.
Core Benefits of Expanding Capacity via Modular Mobile Cleanrooms
- Drastically Shortened Expansion Cycles & Rapid Response Traditional cleanroom construction takes 3–6 months from design to acceptance. In contrast, modular units are prefabricated in the factory. On-site work involves only module splicing and system debugging, shortening the deployment cycle to 15–30 days, with the fastest delivery in 10 days. This is irreplaceable for scenarios requiring rapid capacity boosts, such as emergency public health testing or pre-clinical drug R&D sprints.
2. Reduced Costs & Minimized Resource Waste
- Low Initial Investment: Factory prefabrication reduces on-site labor and material waste. No large-scale renovation of existing labs is needed (units can be deployed outdoors or in warehouses).
- Low Operating Costs: Standardized maintenance and precise energy control reduce consumable and utility expenses.
- High Asset Reuse: Units can be relocated or reused as capacity needs shift, avoiding the “sunk cost” of immovable traditional cleanrooms.
3. Flexible Adaptation to Capacity Fluctuations & Improved Space Utilization The modular design supports “on-demand addition/subtraction.” Labs can combine one or multiple units to form clean spaces of varying sizes based on sample volume or project load. When capacity adjusts, units can be quickly disassembled or added. The mobile feature allows for optimized layout adjustments within existing sites, enhancing space efficiency.
4. Ensuring Operational Continuity & Lowering Risk Expanding with modular units does not require shutting down the existing laboratory. Deployment and debugging occur without disrupting current workflows. Furthermore, labs can pilot a small number of units to verify adaptability before scaling up, avoiding the risks associated with the “one-time massive investment” of traditional cleanrooms.
Detailed Steps to Rapidly Expand Lab Capacity
1. Pre-Assessment
- Define Goals: Determine the target capacity (e.g., daily sample volume, new workstations), required area, and cleanliness level (e.g., Class 10,000 for microbiology).
- Site Survey: Evaluate available space (outdoor ground, indoor warehouse), load-bearing capacity, and utility interfaces to decide on deployment location.
- System Needs: Identify requirements for equipment compatibility, HVAC, and special disinfection (UV, Ozone). Recommendation: Partner with experts like Boben for a comprehensive assessment.
2.Solution Customization & Factory Prefabrication
- Design: Finalize parameters: unit dimensions, quantity, cleanliness class, and auxiliary systems based on the assessment.
- Fabrication: The manufacturer builds the main structure, installs wall panels, and assembles/debugs systems in the factory. Pre-testing (cleanliness, performance) is conducted.
- Site Prep: Simultaneously, the lab prepares the site (leveling ground, utility connections, permits for outdoor temporary structures).
3. On-Site Deployment & System Debugging
- Assembly: Units are transported to the site and assembled via hoisting or splicing (single unit assembly often takes <1 day).
- Connection: Connect utilities and install purification, ventilation, and monitoring systems.
- Debugging: Conduct system tests: Particle counting (cleanliness), calibration (Temp: 20-26°C, Humidity: 40-60%), pressure adjustment (10-30Pa positive pressure), and disinfection testing. This phase takes 3–5 days, followed by certification.
4. Equipment Move-in & Personnel Training
- Installation: Move in lab equipment (biosafety cabinets, incubators), calibrate, and debug to ensure compatibility.
- Training: Train staff on system operation (start/stop, parameter adjustment), maintenance (cleaning, filter changes), and emergency response.
- Trial Run: Conduct pilot experiments to verify capacity improvements and workflow smoothness.
5. Acceptance & Official Production
- Final Acceptance: Verify performance against requirements and officially launch.
- Maintenance Log: Establish a maintenance schedule (weekly pressure checks, monthly filter cleaning) to ensure long-term stability.
- Future Expansion: Repeat steps to add more units if needed.
Practical Results (Case Studies)
Case 1: Third-Party Medical Testing Laboratory Facing a surge in samples due to a public health emergency, the lab needed a 50% capacity increase within 1 month. Using Boben’s Modular Mobile Cleanroom Solution, they customized 2 Class 10,000 units (3 workstations each). On-site deployment took only 12 days. Post-launch, daily capacity increased by 800 samples, efficiency rose by 55%, and all environmental parameters remained stable with no anomalies. After the emergency, the units were relocated to a branch lab, achieving 100% asset reuse.
Case 2: Biopharmaceutical R&D Enterprise To accelerate a new drug project, the company needed 6 new workstations within 2 months. Traditional construction would take 4+ months. Choosing the modular solution, they deployed 3 Class 1,000 units (18㎡ total). Factory prefabrication took 20 days, and on-site setup took 4 days—total cycle 1.5 months. The new space accelerated R&D by 30%, finishing pre-clinical trials 1.5 months early. Energy consumption was 25% lower than traditional cleanrooms, saving ~$4,500/year. Later, 1 additional unit was added in just 3 days, boosting capacity by another 20%.
Case 3: University Environmental Testing Laboratory Undertaking a major heavy metal testing project, the university needed to expand capacity without disrupting ongoing operations. They deployed 2 Class 10,000 units outdoors, equipped with specialized waste gas treatment systems. Deployment took 30 days with zero impact on existing workflows. Heavy metal testing capacity increased by 60% (8 simultaneous sample groups), shortening the project cycle by 40%. After the project, the mobile units were moved to a training base for teaching, maximizing resource utility.